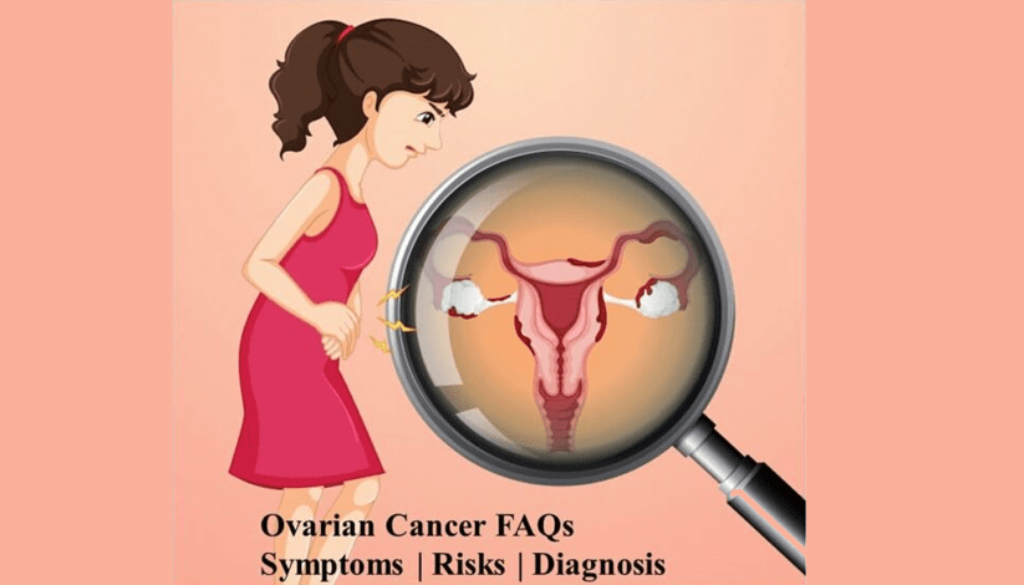
Ovarian Cancer FAQs | Symptoms | Risks | Diagnosis
Ovarian Cancer FAQs | Symptoms | Risks | Diagnosis | Ovarian Cancer FAQs
Ovarian Cancer FAQs | Symptoms | Risks | Diagnosis
Ovarian Cancer FAQs
What are the early signs of ovarian cancer?
The following are the early signs of ovarian cancer:
- Heaviness in the abdomen
- Bloating
- Pelvic pain and abdominal pain
- Changes in bowel movements
- Abdominal swelling
- Frequent urination
What are the typical signs of ovarian cancer?
Some of the typical signs of ovarian cancer include:
Constipation, back pain, fatigue or unexplained exhaustion, weight loss, menstrual irregularities, abdominal swelling, a pressure in the lower back or pelvis, abdominal pressure, increased frequency of urination, lack of appetite, feeling full quickly after starting to eat, abdominal cramps, bloating and painful sex.
What can mimic the symptoms of ovarian cancer?
Back pain, nausea, fatigue, constipation and other gastrointestinal issues like heartburn and menstrual irregularities. Many women tend to ignore gastrointestinal and menstrual issues as regular health concerns and thus delay seeking medical care.
Why ovarian cancer is not detected early?
There is no proper screening test to detect ovarian cancer in the early stage. The next feature of ovarian cancer is that it silently and progressively spreads and causes some common symptoms or no symptoms at all. Another feature of ovarian cancer is quite perplexing; the symptoms such as abdominal pain, gas, constipation, bloating, indigestion, pressure in the pelvis and back are often confused with less serious digestive issues. That’s the reason why the majority of women tend to ignore the early signs and avert consulting a gynaecologist. Therefore, 80% of women miss diagnosis and only 20% of ovarian cancers are diagnosed early.
How is ovarian cancer diagnosed?
A gynaecologist examines the patient thoroughly. She will ask a few questions to the patient. Based on the patient’s medical history and symptoms, she will do a pelvic examination. If she finds something abnormal [an enlarged ovary or signs of fluid in the abdomen (ascites)], during the pelvic exam she will recommend some tests including imaging tests such as ultrasound and CT scans of the abdomen and pelvis, blood tests and tumour marker tests such as CA 125 test. In addition, a biopsy may be done to confirm the diagnosis accurately. Once ovarian cancer is confirmed, the doctor does the staging of ovarian cancer.
Why ovarian cancer does not cause any symptoms in the early stages?
Ovarian cancer remains confined to the ovaries during the early stages. Therefore, it rarely causes any symptoms during the early stages. Symptoms if present, may be mild and subtle. They are mostly related to the symptoms of gastrointestinal issues.
Successful treatment of ovarian cancer is very much possible when it remains confined to the ovary during the early stages.
Ovarian cancer FAQs
Why is ovarian cancer the most challenging cancer?
Ovarian cancer is the most difficult to detect, diagnose and treat for the following reasons:
- It is silent, aggressive, and asymptomatic
- Symptoms if present seems to be less serious
- When it goes unnoticed it becomes life-threatening
- Mostly detected in the advanced stages
- The third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women in India
Ovarian cancer, being silent cancer, can subtly and aggressively spread to pelvis and abdomen. It remains usually undetected during this stage as well. Once ovarian cancer becomes metastatic and aggressively spreads, it becomes fatal and relatively difficult to treat. Malignant ovarian cancer can spread even to the liver and lungs in the advanced stages.
What is a Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS)?
A gynaecologist uses this test to detect any abnormalities in the female reproductive organs – uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. The doctor inserts an ultrasound probe into the vagina. The ultrasound waves produce an image of the uterus, fallopian tubes, vagina and ovaries. Your radiologist, gynaecologist and oncologist use this test to detect abnormalities in the ovaries (solid growth or cysts (fluid-filled sacs)]. If your gynaecologist detects any solid potential growth, she will order a biopsy to confirm whether the growth is non-cancerous (benign) or cancerous.
When should you consult a gynaecologist?
If you are a woman, you should talk to your gynaecologist as soon as you notice any abdominal symptoms. The signs could be some unexplained symptoms of ovarian cancer or any other pelvic or new abdominal symptoms.
You should consult your doctor if:
- You notice any pelvic or abdominal symptoms or any other symptoms unrelated to any other diagnosed condition.
- Indigestion or stomach issues do not improve with diet changes and other lifestyle measures
- Your back pain does not improve with rest and cold compresses
- the symptoms occur for more than twelve days in a month or last for more than two weeks
Is ovarian cancer screening available to detect ovarian cancer in healthy women?
Currently, there are no screening tests available to detect ovarian cancer in women who are asymptomatic or do not have any symptoms.
The major risk is genetically linked (hereditary), how?
- Gene mutations in the BRCA1 gene increases risk up to 40%
- Gene mutations in the BRCA2 gene increases risk up to 18%
Thus, the risk is associated with inherited mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.
How to reduce gene-related (hereditary) risk of ovarian cancer?
Women with a strong family history of ovarian and breast cancers should discuss with their doctor the genetic tests for these gene mutations. Based on the results of the genetic tests, they can opt for prophylactic treatment (ovarian cancer surgery) and minimize their risk and future complications. In addition to genetic analysis and studies, proteomics (the study of protein folding, patterns) research is gaining momentum. To know more ovarian cancer FAQs, read