Screening Tests for Early Detection of Cancer in Women
Cancer screening tests are designed to detect cancer at an early stage, before it causes symptoms and when it is more manageable to cure. Screening tests that are effective include the following:
Breast Cancer Screening Tests
When a lump is too small for you to sense and differentiate and the disease hasn’t spread to other regions of your body, a breast cancer screening test can typically detect breast cancer.
Mammogram
This is the most common approach for doctors to detect breast cancer. It creates images of the interior of your breasts using X-rays. A 3D mammography consists of many images that allow your doctor to observe your breast from various angles.
One breast at a time will be placed on a separate platform by a specialist. Then a translucent plastic paddle will be used to stretch your breasts out. This is done to ensure that the X-ray captures all of your tissues. You may need to shift postures so that the technician can take photos from various angles. For a few seconds, you’ll have to hold your breath.
Consult your doctor if you have a higher risk of breast cancer due to family background or other factors. You may require mammograms earlier and more frequently than these recommendations suggest. Other cancer screening tests, such as an MRI, may be required.
Self-examinations of the breasts – A majority of women don’t do breast self-examination. If you want to get to know your breasts better, consult a doctor about what you should look for and check.
Colorectal cancer
Colonoscopy, stool tests, and sigmoidoscopy: Several cancer screening tests have been found to minimize the chances of colorectal cancer. Colorectal cancer can be detected early via sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy, and it can be prevented too. Since these tests can detect abnormal colon growths (polyps) that can be eliminated before they turn cancerous. Women who are at risk for colorectal cancer should be screened using one of these tests. The test is recommended for women between the age of 45 and 70 years.
Colonoscopy
A flexible tube with a lens on the end will be used by your specialist to examine your entire colon and rectum. You’ll need to do some planning ahead of time. You’ll only be supposed to drink liquids for a day or two before the procedure, and you’ll take a sedative to empty out your colon.
Sigmoidoscopy
It’s similar to a colonoscopy, although it’s not as thorough. Only approximately a third of your colon can be examined by your doctor. On the plus side, you don’t need to prepare as much and can typically stay awake. It takes roughly 20 minutes to complete this test.
DNA test – A DNA testing method is common, but the lab will additionally look for traces of polyps or cancer cells with gene alterations.
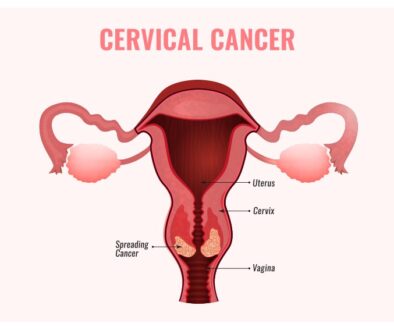
Cervical Cancer
It begins in the cells that line your cervix or lower section of your uterus. Your doctor can frequently detect these gradually altering cells using one of these tests before they cause problems.
Pap screening test
Your feet are on the leg rests as you lie on a table. A speculum is inserted into your vagina to enlarge it enough for your clinician for seeing your cervix. They will then brush or scrape a tissue sample away using a special scraper or brush. It’s possible that you’ll feel a little uncomfortable. The cells are taken to a lab where they are tested for malignancy.
HPV (human papillomavirus) test
It can be done at the same time as the Pap test and with the same cells taken. The lab examines you to discover if you’ve been infected with HPV, the bacteria that causes the majority of cervical cancers. Females should obtain a Pap test every three years starting at the age of 21. Some people may be able to have a Pap and HPV test every 5 years starting at the age of 30. Based on factors such as your age, test record, and probability of developing cancer, your doctor will recommend the best course of action for you.
Lungs Cancer
It’s the most lethal cancer in females, and it’s no secret that smoking is a key contributing factor. If you smoke cigarettes on a regular basis, you should consult a doctor about getting a screening test if you’ve not already.
A low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) scan is used to screen for lung cancer. It takes photos of your lungs with X-rays. It’s a simple process. As the table travels past the scanner, you lie on your back and lift your arms above your head. While it’s being done, you hold your breath for 5 to 10 seconds.
Skin Cancer
The USPSTF has no recommendations for or against skin screenings. However, the American Cancer Society claims that regular doctor visits are an effective approach to detecting skin cancers early. Check with your doctor how often you should receive a skin inspection if you’ve had the condition before or if you have a family history of skin cancer. Your doctor will evaluate your skin for any cancerous moles or other abnormal cells. At least once a month, you should inspect your skin for changes.
Bottom Line
Many women don’t like being screened for cancer due to a fear of positive results or abnormal findings. However, specialists recommend that women should become positive and go for regular health checkups and cancer screening tests. They must get tested for breast cancer and also go for uterine and cervical cancer screening after consulting their gynaec oncologist. Early detection of cancer provides effective treatment in the initial stages itself.