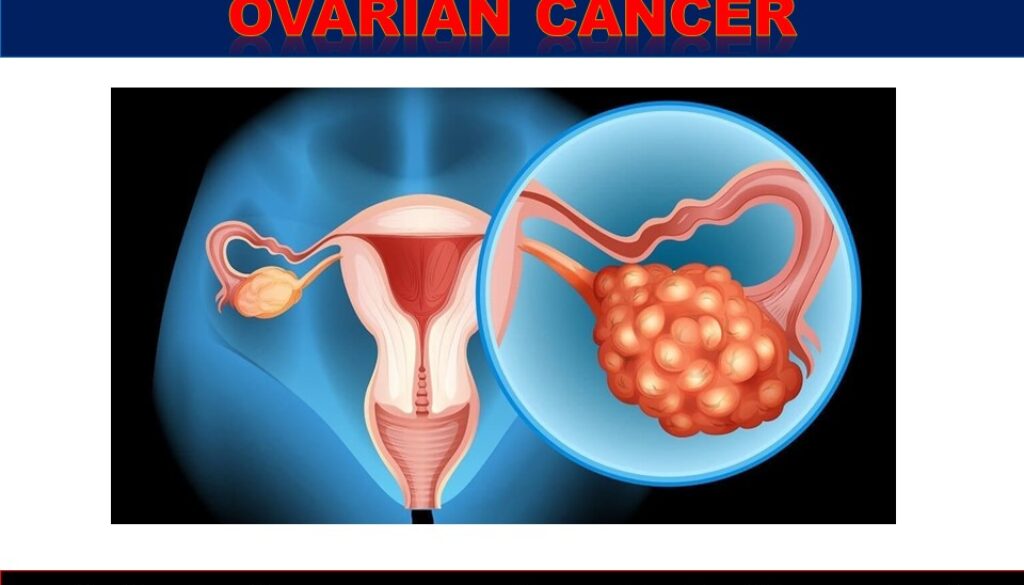
What Every Woman Must Know About Ovarian Cancer?
Being a woman Put You at an increased risk of these health conditions.
What Every Woman Must Know About Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer is the third most commonly detected cancer in Indian women apart from Breast and cervical cancers that top the list. The mortality rate associated with ovarian cancer is high in India. In almost 60% of the cases, the diagnosis of ovarian cancer is made in the later stages of cancer – III or IV stages of cancer. This is quite common in India. Owing to the above factor, the 5-year survival rate for ovarian cancer, in India is very pathetic – which is only 45%. However, early diagnosis is key to successful treatment.
The Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer
Though ovarian cancer mainly affects older women (age above 63 years), relatively younger women with a strong family history are also at higher risk. In general, the major risk factor for ovarian cancer is a family history of ovarian cancer. Therefore, a woman’s family history is taken into consideration while evaluating the lifetime risk of getting ovarian cancer. The other risk factors include:
- Age – In most cases develops after menopause
- Late pregnancy
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Endometriosis
- Use of fertility & Hormone medicines
- Nulliparity – never being pregnant
- Having lynch syndrome
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
- Late pregnancy and having a child after 35 years of age
Ovarian cancer is hereditary – The risk of developing ovarian cancer increases in women by around 65% to 35% if they carry inherited genes variants of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.
For women at relatively higher risk, genetic tests are available to screen the risk of developing ovarian cancer. They should consultant their gynaecologists about the genetic testing to know whether they carry BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes which may increase the risk of developing ovarian cancer. In women who carry these inherited genes, surgical removal of ovaries and fallopian tubes can help reduce the risk of developing ovarian cancer. This can be done after the childbearing years are past.
Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
The symptoms associated with ovarian cancer can develop at any stage of the disease, but in most cases tend to manifest at the later stages – especially when the cancerous growth puts pressure on the uterus, bladder, abdomen and rectum. The warning signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer include:
- Abdominal pain or pressure
- Pelvic pain
- Pressure in the lower back or pelvis
- Abdominal cramping
- Bloating
- Lack of appetite
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Indigestion or upset stomach
- feeling full quickly after starting to eat
- Frequent urination
- unexplained exhaustion
- back pain
- Menstrual changes
- painful sex
- increase abdominal girth or abdominal swelling
- weight loss
The irony of the symptoms associated with ovarian cancer is that such symptoms can be due to several other health issues. However, if the symptoms are not responding to basic treatment or persisting for long or continuing more or less daily irrespective of treatment, then consult a Gynaec oncologist or lady surgical oncologist as they could be warning signs of ovarian cancer.
Early Diagnosis is Key to Successful Treatment
Ovarian cancer does not cause any noticeable symptoms in the early stages.
It grows silently – and therefore, early diagnosis is a key to successful treatment. In cases where cancer has not spread outside the ovary – the 5-year survival rate is nearly about 92%.
An oncologist, gynaec-oncologist or surgical oncologist is involved in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer. The doctor asks the patient about all the symptoms during the medical examination – such as how they began, how long they persist and responded to basic treatment. Next, the gynaeconcologist goes through the patient’s medical history and family history – and then performs a pelvic examination to see whether the ovaries are enlarged, inflamed or whether there is fluid in the abdomen. If the doctor finds any abnormalities during the pelvic examination, then she will order additional tests.
Oncologists recommend the following tests to detect ovarian cancer: Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS); CA-125 blood test – CA-125 protein is a tumour marker – by which the amount of this protein in the blood is measured;
Computed tomography (CT) scans also helps in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer
Biopsy is the usual way to diagnose ovarian cancer.
Treatment
The main treatment for ovarian cancer involves surgery and chemotherapy. Radiation therapy, hormone therapy and targeted therapy are the other treatment options.
Bottom line
Ovarian cancer remains confined to the ovaries during the early stages. Successful treatment of ovarian cancer is very much possible when it remains confined to the ovary during the early stages.
During the early stages, ovarian cancer that remains confined to ovaries rarely causes any symptoms. Being a silent killer, it subtly and aggressively spreads to pelvis and abdomen in the advanced stages. It remains usually undetected during this stage as well. Once ovarian cancer becomes metastatic and aggressively spreads, it becomes fatal and relatively difficult to treat. Malignant ovarian cancer can spread even to the liver and lungs in the advanced stages. Owing to this reason, the majority of the ovarian cancers are diagnosed in advanced stages. The symptoms associated with ovarian cancer are mostly non-specific even in advanced cases.