Cervical Cancer Causes Risk Factors Symptoms and Treatments
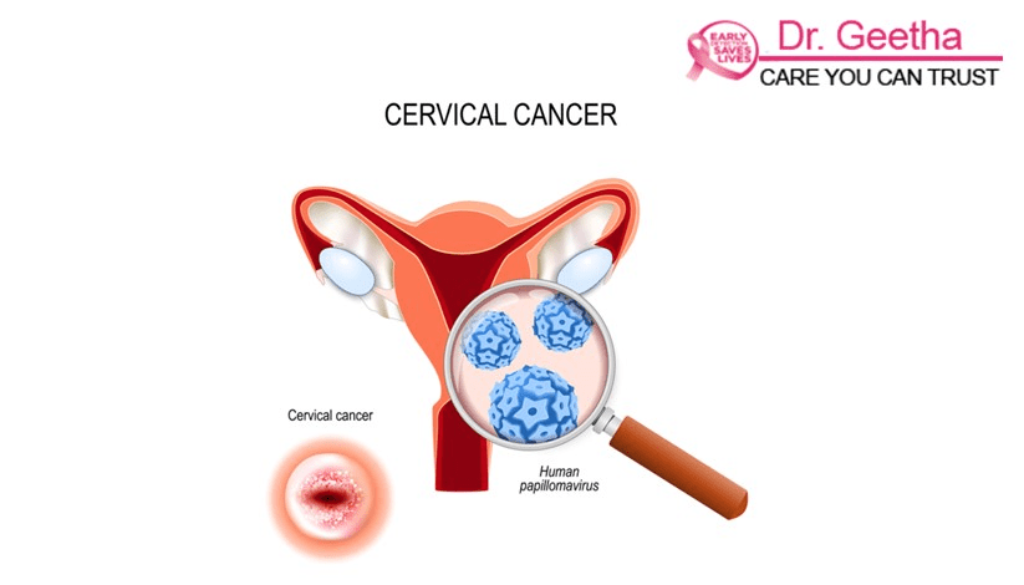
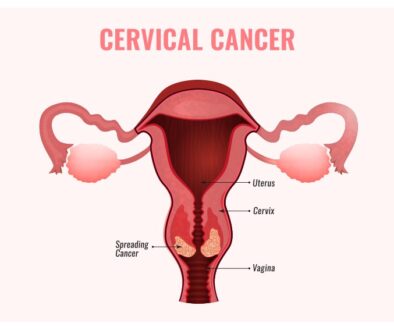
Cervix: It is the lower part of the uterus in the female reproductive system. It connects the vagina and the uterus
Cervical Cancer Causes Risk Factors Symptoms and Treatments
Cervical Cancer Treatment in Hyderabad
Cervix: It is the lower part of the uterus in the female reproductive system. It connects the vagina and the uterus. It mainly comprises fibromuscular tissue. During childbirth wide dilation of the cervix allow the baby to pass through and during menstruation, the cervix opens a little bit to allow menstrual blood to flow.
The following conditions affect Cervix:
Cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix due to herpes, gonorrhoea and chlamydia infections). These are sexually transmitted infections.
PID – Pelvic inflammatory disease. When the infection of the cervix spreads to the uterus and fallopian tube. It is known as a pelvic inflammatory disease.
Cervix polyps – These are abnormal masses or growths on the cervical region that connects to the vagina. Polyps can cause vaginal bleeding, but they are relatively harmless.
Cervical incompetence – During pregnancy, the cervix may dilate or open early. This may lead to premature birth.
Cervical Cancer
When cervical cells become abnormal and grow in an uncontrollable manner cervical cancer develops. During regular pap smears, cervical dysplasia (abnormal growth of the cervical cells) is often discovered. Doctors perform additional tests to detect whether the abnormality is cancer or something else.
The cervical region is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Cervical cancer mostly develops in this region.
HPV (Human Papillomavirus)
In most cases of cervical cancer, several strains of the HPV (Human papillomavirus) play an important role. In some individuals, the virus remains latent for years without causing any damage to the body as the body’s immune system fight against it; but, in some people, the virus may survive for years and thus contribute to the development of cervical cancer.
Some virulent strains of human papillomaviruses (a group of viruses) play a major role in the development of cervical cancer – other less virulent strains cause cervical and genital warts.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
The signs and symptoms associated with cervical cancer do not manifest during the early stages as cancer goes symptomless during the initial stages.
The symptoms that are mostly seen in the advanced stages include the following:
- Pain during intercourse
- Pain in the abdomen or pelvic region
- Heaviness in abdomen
- Bloating, fullness and swelling
- Changes in bladder or bowel movements
- Frequent urination
- Heavy vaginal discharge may be watery, heavy and bloody and it has a foul odour.
- Weight loss
Cervical Cancer Causes
Healthy cells in the cervix grow and multiply at an abnormal rate due to mutations. Mutated cells form a growth or mass of cells. The abnormal mass of cells turns into cancer. The cells from the tumour aggressively multiply and invade nearby tissues and even spread outside the cervix to the uterus, fallopian tubes and also to other parts of the body. It is not well-established as to what causes cervical cancer, but the role played by the HPV virus has been established. The HPV virus is common in many people – and, it doesn’t always develop cancer. Therefore, other factors (lifestyle and environmental factors) can also play a role.
The Risk Factors for Cervical Cancer
The following are the risk factors for cervical cancer:
- Sexual encounter at an early age increases the risk
- Multiple sexual partners
- Sexually transmitted diseases such as syphilis, gonorrhoea, HIV/AIDS and chlamydia can increase the risk of HPV.
- Low immunity due to an immune disorder or any other health condition
- Smoking and drinking
Diagnosis of cervical cancer
Pap Test
A gynaecologic oncologist performs a pap test to look out for the abnormalities present in the cervix. Cells taken out from the cervix of a woman are examined to detect changes.
Colposcopy
A gynaecologist recommends a follow-up test if she finds any abnormality in the Pap test. It is known as colposcopy. The gynaecologist uses a special instrument with magnifying lenses (colposcope) to carefully examine the abnormal areas of the cervix. During this procedure, a very small amount of tissue is taken (biopsy) out and send to the laboratory for checking whether the sample has abnormal cancerous growth.
Cone biopsy
It is another test recommended by oncologists following an abnormal Pap test. In this procedure, a very small cone-shaped (mostly triangular) tissue is removed from the cervix and sent to the laboratory for microscopic examination. It is employed to both remove abnormal cells and to identify those cells.
CT Scanning
A CT scanner takes several photographs (X-rays) of the cervical region and then creates a detailed picture of the cervical region and also the area surrounding cervix – abdomen and pelvis. Cervical cancer sometimes becomes aggressive and silently spreads to these surrounding tissues. Therefore, to know the extent of its spread, CT scanning is recommended by the surgical oncologists.
MRI Scan
To obtain high-resolution images of the entire cervical area and also the area surrounding the cervix – pelvis and abdomen a high-powered MRI scanner is used. It is known as MRI scan – Magnetic resonance imaging. It helps in determining the spread of cervical cancer to local organs and other areas of the body.
PET CT Scan
To get further details about the spread of cervical cancer, oncologists recommend PET (Positron emission tomography) scan also. This scan is done after a tracer solution containing a mildly radioactive chemical is injected into the veins of the patient. The cancerous cells present in the body take up the tracer and appear light in the scanned images. The scanner takes the images of such areas.
DNA testing for detecting HPV: In this test, the sample is tested for the presence of Human Papilloma Virus DNA. The test is recommended to detect the presence and types of HPV viruses that can cause cervical cancer.
Cervical Cancer Treatment in Hyderabad
Treatment depends on the patient’s age, the stage and type of cancer and the extent to which cancer has spread in the body. The standard treatments for cervical cancer include Surgery, Radiation therapy, Chemotherapy, Targeted therapy and Immunotherapy. Treatment for a recurrent cervical cancer may include chemotherapy to alleviate symptoms – mostly as palliative therapy; chemotherapy and targeted therapy; radiation therapy and chemotherapy, immunotherapy and pelvic exenteration.
Prevention of Cervical Cancer
Regular pap smears can prevent cervical cancer in most women. Regular screening helps in detecting precancerous growth at an early stage – where treatment ensures optimal results. Furthermore, after detecting any precancerous conditions, monitoring them becomes easier. Therefore, physicians recommend that pap smears should be routinely done after age 21. It should be repeated after every few years.
Among cervical cancer causes, HPV is the prominent one. Practising safer sex is very important as it reduces the risk of cervical cancer in two ways: first by preventing the spread of sexually transmitted diseases and second by preventing the spread of HPV.
If you have any concerns regarding the symptoms, causes, diagnosis and cervical cancer treatment in Hyderabad, consult:
Dr. Geetha Nagasree
Cervical Cancer specialist in Hyderabad