Cancer in India remains a Bewildering Puzzle for Oncologists
Most common cancer in women: India is witnessing an increasing number of cancer cases with a startling figure of over 1.5 million new cases
Cancer in India remains a Bewildering Puzzle for Oncologists
Most common cancer in women: India is witnessing an increasing number of cancer cases with a startling figure of over 1.5 million new cases every year – the mortality rate associated with all types of cancers is high compared to advanced countries of the world. Though the number of cancer cases per 100000 people in the US is high (300 cases per 100000 people) when compared to India (100 cases per 100000 people), the five-year survival rate is quite low in India. Breast cancer is the most common cancer in both urban and rural India.
Another puzzling trend in India is that more women are being diagnosed with cancer then men in contrary to the global statistics wherein cancer incidences are 25% higher in men than women.
Rising Incidences of Cancer in Women is a Cause for Concern
Most common cancer in women: More than 70% of cancers in women in India are breast, cervical, ovarian and uterine cancers. These cancers can be treated effectively if detected early – and thus the chances of survival increases, but the irony is that these cancers are often diagnosed at an advanced stage – owing to which the five-year survival rate is quite low. Both oral and lung cancers are common in men and these are mostly related to lifestyle (smoking and chewing tobacco). In men, the survival rate is quite low as both lung and oral cancers are more potent.
As far as breast cancer is concerned, it accounts for nearly about 30% of all cancer cases in women with a very sharp rise in cases over the last five to six years. Furthermore, the worrisome fact is the shift in the age bracket as a younger woman are being diagnosed with breast cancer more often than ever.
The shift in Peak Age
The peak age for the onset of breast and ovarian cancer in India has been shifted to 40 years from 45 years a few years ago – which appears to be a decade younger than elsewhere in the world. The recent shift in the age of onset can be attributed to lifestyle, genetic, environmental, and other factors.
Are We Fighting the Cancer Right Way?
The biggest challenge is the age shift, least awareness, and late diagnosis of gynaecological cancers in women. Late diagnosis in many cases is attributed to the fact that many women tend to postpone seeing a doctor as most of the cancers in the early stages do not show any symptoms.
Women must focus their attention on the preventable cancer-causing factors such as high-fat diet, obesity, late marriage, fewer children, and inadequate breastfeeding – and, take appropriate measures. They can talk to their oncologists in this regard.
Five Year Survival Rates are Poor in India
If we take the example of US, more than 80% cancers are diagnosed in the early stages (first and second stages), whereas in India breast, cervical and ovarian cancers are diagnosed in the third and fourth stages. Owing to this reason only 50% of women in India survive for less than five years.
Cancer Screening Still Remains the Best Tool to Arrest Cancer
Owing to the increase in the number of breast cancer cases throughout the world, women falling under the age group of 20 to 30 years should consider having breast examination done by a health care provider every two years and if they come from high-risk family, then the frequency of breast examination should be once in every year. (Mammography for women above 35 years is required).
PAP Test (PAP Smear)
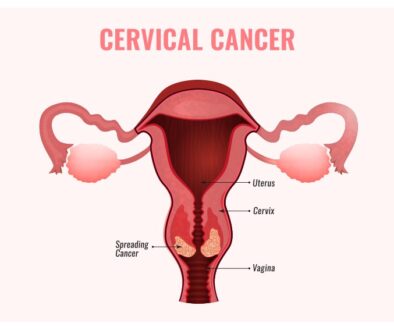
PAP test –For women age 30 and above a combined PAP and HPV test is recommended. In the absence of an HPV test, a PAP test can be done every 3 years. Pap test helps identify women at risk for developing cervical cancer. PAP test in combination with HPV test help in identifying women who are at increased risk of developing cervical cancer.
Pelvic Examinations to Prevent Cervical Cancer
Women should consider undergoing pelvic examination – based on medical history and other risk factors. However, regular health check-ups and consultations with gynaec oncologists should be a part of preventive healthcare. This will help in assessing overall health, lifestyle, and other risk factors.
HPV and Cervical Cancer
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the causative agents of cervical cancer. It accounts for nearly about 25% of all cancers in women. It can be easily tackled as the HPV vaccine is available to prevent it.
The most common cancer in women in India includes breast, cervical, ovarian, and uterine cancers.