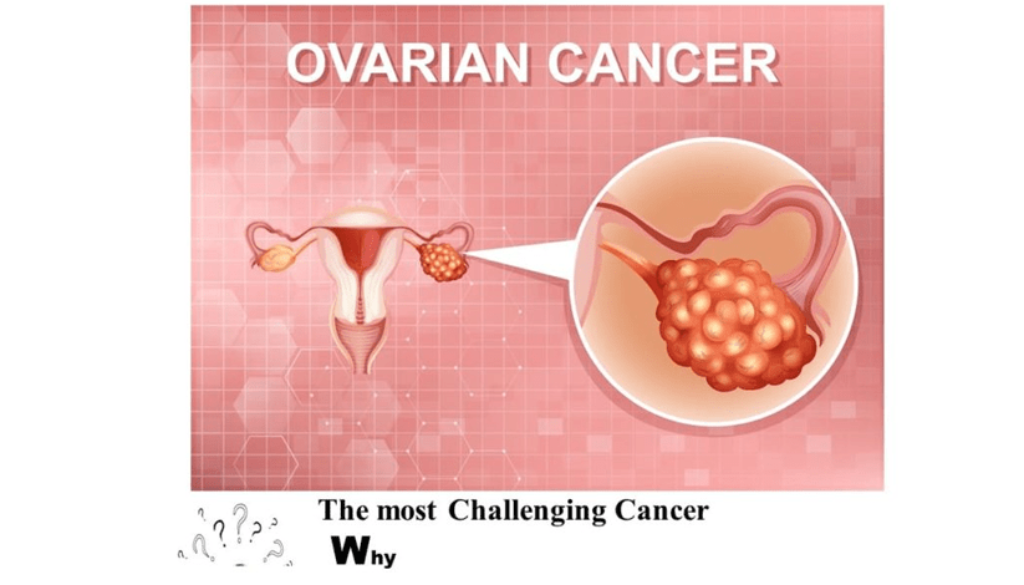
Why Ovarian Cancer is the most Challenging Cancer
Why Ovarian Cancer is the most Challenging Cancer?
Why Ovarian Cancer is the most Challenging Cancer?
Ovarian Cancer Hyderabad | Dr Geetha Nagasree
Late detection of cancer is a major cause of concern in India. A majority of women succumb to cancer (ovarian, uterine, breast and cervical) due to advanced stage detection and ineffective treatment.
We will try to answer the following questions here:
Is it the unawareness or some other factors that hinder the timely diagnosis of cancer in women?
What needs to be done to stop the increasing numbers of breast, ovarian and cervical cancer cases in India?
Ovarian cancer – The most challenging cancer in women. Let us understand why ovarian cancer is difficult to detect, diagnose and treat.
- It is silent, aggressive, and asymptomatic.
- Symptoms if present seems to be less serious.
- When it goes unnoticed it becomes life-threatening.
- Mostly detected in the advanced stages.
- The third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women in India.
What happens if cancer is not detected early?
If cancer is not detected early, it grows silently and aggressively, and then leads to advanced stages. A full-blown metastatic cancer (cancer spread to other organs) becomes difficult to treat.
The majority of women miss rather ignore some less serious and common warning signs and symptoms of cancer. The symptoms are either subtle or look similar to the symptoms of some common stomach problems. Therefore, it’s quite natural for women to miss such warning signs.
There are some factors that hinder a timely diagnosis of ovarian cancer in women.
Let us try to understand some of those.
The reasons for the late detection of ovarian cancer
- Non-availability of screening tests
- Ovarian cancer progresses silently
- Symptoms are either absent or seem to be less threatening
- Symptoms look similar to the symptoms of other common health issues
- Bloating, gas, constipation and stomach pain are often confused with stomach problems
- The majority of women tend to ignore the early warning signs
- Less serious symptoms go unnoticed by many women
- The majority of women tend to delay consulting a specialist
- A whopping 80% of women miss the diagnosis
- Only 20% of women meet specialist doctors
Ovarian Cancer Facts
- Symptoms may or may not present
- Symptoms mostly look familiar (tummy upset)
- Symptoms if present, look mostly non-specific even in the advanced stages
- The major risk factor is genetically linked (hereditary)
- The risk is associated with inherited mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.
- The primary treatments are surgery and chemotherapy
- Radiation, hormone therapy and targeted therapies are the other treatment options
The Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer
- Main: Family history of ovarian cancers
- The overall risk (gene-related) is 15%
- Gene mutations in the BRCA1 gene increases risk up to 40%
- Gene mutations in the BRCA2 gene increases risk up to 18%
- Other risk factors: Early menstruation (menarche)
- Late menopause
- Women who never got pregnant are at risk
- Hormone replacement therapy after menopause
- Obesity
- Endometriosis
- Advancing age
- Infertility
- Women who took estrogen for more than 10 years are at risk
Warning Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
- Changes in urination patterns, such as more frequent urination
- Unusual vaginal bleeding
- Pressure or pain in the abdomen
- Feeling full rapidly when eating
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating (indigestion)
- Constipation
- Changes in bowel habits
- Pressure or pain in the pelvis
- More frequent urination (changes in urination patterns)
Causes of Ovarian Cancer
Cells in the ovaries grow and multiply abnormally into a mass of cells (lump of tissue. The exact cause (why this happens) is unknown.
Endometriosis – endometrium grows into ovaries and fallopian tubes and may cause ovarian cancer.
Types of Ovarian Cancers
There are several types of ovarian cancers and the three most common among those include epithelial cells, germ cells and stromal cells ovarian cancers.
Epithelial cells tumours: develop from the outer covering of the ovaries.
Germ-cells tumours: develop from the germ cells of the ovaries.
Stromal cells tumours: develops from the stromal cells.
Germ cells and stromal cells tumours are rare.
Epithelial cells tumours often become malignant (cancerous) and spread to other organs (metastasize). Malignant tumours are fatal. In the advanced stages, malignant epithelial cells tumours can spread to the abdominal and pelvic region and also to the liver and lungs.
Benign (non-cancerous) ovarian tumours may not spread beyond ovaries.
Is Screening possible?
Screening women for ovarian cancer is a bit challenging for researchers and oncologists -owing to the fact that there is no proper screening test available. However, women with a strong family history of ovarian and breast cancers should discuss with their doctor regarding genetic tests for these gene mutations. Based on the results of the genetic tests, they can opt for prophylactic treatment and minimize their risk and future complications.
Researching is continuously working hard to find new ways to screen women for ovarian cancer. In addition to genetic analysis and studies, proteomics (the study of protein folding, patterns) research is gaining momentum.
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer
A gynaec oncologist order the following tests for the diagnosis of ovarian cancer: ultrasound and CT scans of the pelvis and abdomen, blood tests and tumour marker tests such as CA 125. A biopsy is also ordered to confirm the diagnosis accurately. After confirmation of the diagnosis, the doctor performs the staging of cancer.
Newer Diagnostic Approaches
The use of new imaging techniques such as Functional MRI is being evaluated in ovarian cancers. PET/CT scans are also being studied to see where they may be best used for ovarian cancer.
Treatment for Ovarian Cancer Hyderabad
The treatment for ovarian cancer involves surgery, chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy and radiation therapy.
Treatment depends on the general health of the patient, the location of cancer and the extent of its spread. Early-stage cancer is treated with surgery. For a woman of childbearing age, if the cancer is detected in the early stage, it is possible to treat cancer without removing ovaries and uterus.
Robust Treatment Approaches
Relapsing and recurring ovarian cancers demand robust treatment approaches. Therefore, for the treatment of advanced stage, recurring ovarian cancer, new chemotherapy drugs, or a combination of drugs are being used. Now, the biggest challenge for oncologists treating advanced-stage ovarian cancer is the slow response to chemotherapy. To counter this challenge, HIPEC is gaining momentum. A combination of cytoreductive surgery with HIPEC is the most effective treatment for ovarian cancer (Hyderabad).
Bottom Line
If cancer is detected late – the survival rate is low and the cost of treatment will be higher. In general breast, ovarian and cervical cancers are detected late in the advanced stages. Therefore, the need of the hour is the timely diagnosis, effective treatment and palliative care to address the growing incidences of breast, cervical and ovarian cancers in India.
Dr Geetha Nagasree
MBBS, MD, M Ch (Surgical Oncology)
Senior Consultant Surgical Oncologist
Care Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad
Book an appointment | Ovarian Cancer (Hyderabad) | Dr Geetha