Ovarian Cancer Vs. Ovarian Cysts – FAQs
Ovarian cancer Vs Ovarian Cysts
A malignant growth that arises from the ovarian cells or nearby tissues is known as ovarian cancer. The cancerous growth can arise from the ovarian cells’ surface – it is known as epithelial ovarian cancer from the fallopian tube and also from inside the lining of the abdomen that surrounds many abdominal structures.
Liquid or semisolid-filled sac-like structures that are closed within the ovary are called ovarian cysts. Both ovarian cysts and ovarian cancer do not cause any discomfort or produce any symptoms when they remain small. However, once they grow and become very large or when cancer has advanced then the symptoms may manifest. Both these conditions often share similar symptoms.
How to figure out when one has ovarian cancer? Or how can ovarian cancer be detected early?
A gynaec oncologist order the following tests for the diagnosis of ovarian cancer: ultrasound and CT scans of the pelvis and abdomen, blood tests, and tumor marker tests such as CA 125. A biopsy is also ordered to confirm the diagnosis accurately. After confirmation of the diagnosis, the doctor performs staging of cancer. MRI and PET/CT scans are the newer diagnostic approaches.
What are the causes of ovarian cysts?
There are many reasons for the development of ovarian cysts including endometriosis, menstrual abnormalities, infertility, hypothyroidism, oral contraceptives, birth control methods, and benign growths in the ovaries.
Ovarian Cancer Vs Ovarian Cysts – What are the common symptoms?
- Abdominal bloating
- Abdominal discomfort
- Pelvic pain or
- Abdominal pressure (lower abdominal pressure)
- Pain with sexual intercourse especially with deeper penetration
- Feeling full early when eating
Are ovarian cysts harmful?
Most the ovarian cysts are harmless, but some may cause problems such as pain, torsion, bleeding, or rupture,
What is the difference between an ovarian cyst and ovarian cancer with regards to symptoms?
Ovarian cancer vs Ovarian cysts: It is very difficult to distinguish both these conditions only on the basis of symptoms.
What are the first signs of ovarian cancer?
The most prominent early sign of ovarian cancer is abnormal menses or menstrual irregularity.
What are the late symptoms of ovarian cancer?
The Symptoms that manifest later include:
- Feeling full after eating little
- Loss of appetite
- Constipation
- Nausea and vomiting
- Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen (Ascites). It may cause abdominal distension and shortness of breath
- Abdominal swelling
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Abdominal bloating
- Urinary frequency
- Pain with intercourse
- Gas and/or diarrhea
Can an ovarian cyst cause sciatica-like back pain?
Yes, an ovarian cyst can cause lower back pain that can radiate to the thighs and legs.
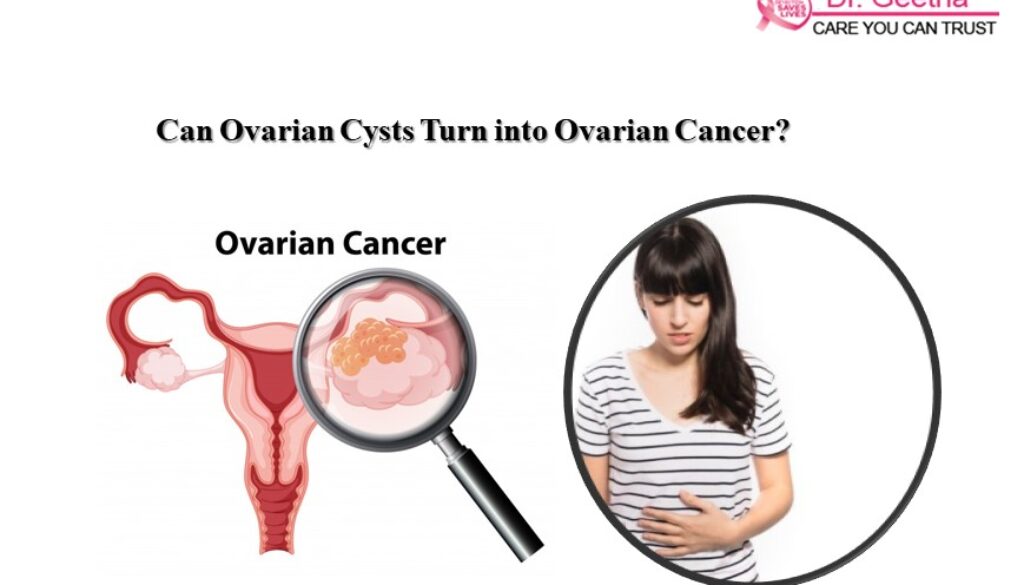
When do ovarian cysts become cancerous?
Most ovarian cysts are benign (non-cancerous); however, rarely, ovarian cysts may be related to ovarian cancers.
Read more…
Very important information “Can Ovarian Cysts Turn into Ovarian Cancer?”
What should I do if I have an ovarian cyst?
Doctors monitor ovarian cysts with a wait and watch approach if the cysts are small and do not become large or cause any symptoms. However, if cysts become large and cause symptoms, then they are removed surgically.
Can ovarian cancer be prevented? How?
Learn – How to Prevent Ovarian Cancer.
Is the Cause of Ovarian Cancer Known?
In the majority of cases, the cause of ovarian cancer is unknown or unclear. However, there are certain risk factors such as gene mutations in the BRCA1 gene and a family history of ovarian and breast cancers.
What are the symptoms of ovarian cysts?
Ovarian cysts do not cause any symptoms unless they are large or rupture or twist when they become large. The symptoms associated with a large or ruptured cyst include the following:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Infertility
- Indigestion
- Heartburn
- A feeling of abdominal fullness
- Bloating
- Abdominal distension
- Abdominal tenderness
- Feeling pressure to have a bowel movement
- Problems having bowel movements
- Vaginal pain or spotty bleeding from the vagina
- Pelvic pain or pressure following vigorous activity or exercise
- Problems with the control of urination
- Pressure or pain with bowel movement or urination
- Chronic pelvic pain or low back pain throughout the menstrual cycle
- A feeling of lower abdominal or pelvic pressure or fullness
- Lower pelvic pain or abdominal pain.
- Pelvic pain may be intermittent or can be severe, sudden, and sharp
Bottom Line
To know more about Ovarian cancer vs ovarian cyst, book an appointment for a personal meeting. if you have any concerns regarding ovarian cyst or cancer – don’t hesitate to call.